Archive for the ‘linux’ Category
Install, configure and run SVN server on Linux
This note is about how to install, configure and run SVN (Subversion) server on Linux. In my case, it’s Debian.
The requirements:
- Use svnserve, so access repositories via svn:// protocol.
- Install, configure and run SVN server as fast as possible.
Install SVN (Subversion) server
sudo apt-get install subversion |
Create the folder for repositories
In this example repositories are located in /var/spool/svn/, you may choose the another folder.
sudo mkdir /var/spool/svn |
Create the first repository
In the code below, the new repository is created in the test folder.
sudo svnadmin create /var/spool/svn/test |
Configure access
Find /var/spool/svn/test/conf/svnserve.conf and check that password-db, anon-access and auth-access are uncommented and have the following values:
password-db = passwd anon-access = none auth-access = write |
Set users passwords in repository’s passwd file:
[users] user1 = passwordforuser1 user2 = passwordforuser2 user3 = passwordforuser3 |
Start SVN server with help of svnserve
svnserve -d -r /var/spool/svn |
Possible problems:
1. If you cannot checkout and get the error, use the correct path.
user@server:~$ svn co svn://server.url/var/spool/svn/test ~/test |
svn: No repository found in ‘svn://server.url/var/spool/svn/test’
Incorrect repository path. It should be:
user@server:~$ svn co svn://server.url/test ~/test |
2. If you get an access error check the repository access configuration.
user@server:~$ svn co svn://server.url/test ~/test --username user1 --password 123456 |
svn: No access allowed to this repository
No access to this repository. Check that password-db is uncommented in svnserve.conf and auth-access has the value of write:
password-db = passwd auth-access = write |
Also check that you have the user password configuration in passwd file of the repository.
Remote backup and restore SVN repository
Backup:
sudo svnrdump http://some.url/some-repository > backup.dump |
Restore:
sudo svnadmin load repository_name < ~/backup.dump |
Useful links
Configure DKIM on Postfix
Here are steps to configure DKIM on Postfix.
I configure DKIM on Postfix using the Ubuntu.
1. Install dkim
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install opendkim opendkim-tools |
2. Configure /etc/opendkim.conf
Domain yourdomain.com KeyFile /etc/mail/mail.private Selector mail |
3. Configure /etc/default/opendkim file
Add to the end of the file.
SOCKET="inet:8891" |
4. Configure /etc/postfix/main.cf file
Add these configuration options to the end of the main.cf file.
# DKIM milter_default_action = accept milter_protocol = 2 smtpd_milters = inet:localhost:8891 non_smtpd_milters = inet:localhost:8891 |
5. Create directory /etc/mail and go there with cd
6. Generate keys in /etc/mail
sudo opendkim-genkey -t -s mail -d youdomain.com |
After generating keys you’ll have mail.private and mail.txt in the directory. mail.private is your private key and mail.txt is the public key that you should set as TXT record of the domain.
7. Configure your domain TXT record for DKIM
mail.txt contains what you should set for the domain. It contains something like this:
mail._domainkey IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; t=y; p=MIG...QAB" ; ----- DKIM key mail for youdomain.com |
This means that you need to create TXT record for you domain that has mail._domainkey as a “host name” and v=DKIM1; k=rsa; t=y; p=MI…AQAB as a “ip address/url”.
7. Start opendkim and restart Postfix
sudo service opendkim start sudo service postfix restart |
8. Useful links
Short ssh alias to access to remote host via ssh
Often, when I want to access my remote DigitalOcean server I have to find out the IP address of it. It isn’t comfortable for me so I decided to create a short alias for this IP in /etc/hosts. Now, after I’ve just made an alias, it’s really more comfortable and faster to login to the remove server via ssh.
/ets/hosts
localhost
infous-desktop
your_alias
|
Login via ssh using the alias
ssh
|
UPDATE:
The another way to set the ssh alias is to edit the ~/.ssh/config file.
Host your_alias Hostname |
Then to login just type:
ssh
|
But there’s a shorter way. Again, edit ~/.ssh/config and set:
Host your_alias Hostname User your_user |
Now, you can login to your remote host via ssh like:
ssh your_alias
|
Thanks to everybody that commented this little note and suggested more elegant solutions!
Install PhpStorm on Ubuntu
I use Ubuntu 11.10 and in this short note I will provide steps to install PhpStorm.
1. Install Java
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer |
And check that Java’s been installed well:
java -version
|
Or:
javac -version
|
http://www.webupd8.org/2012/01/install-oracle-java-jdk-7-in-ubuntu-via.html
2. Download PhpStorm for Linux. You will download PhpStorm-5.0.4.tar.gz or something like this. BTW, I download it using Google Chrome.
http://wiki.jetbrains.net/intellij/Installing_and_running_PHPStorm_on_Ubuntu
3. Click on the downloaded archive so that Archive Manager will be opened. Extract all files to ~/PhpStorm/ if you don’t have this folder create it.
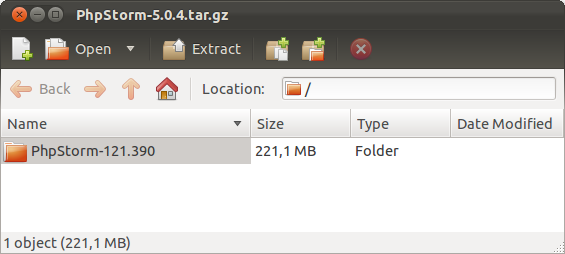
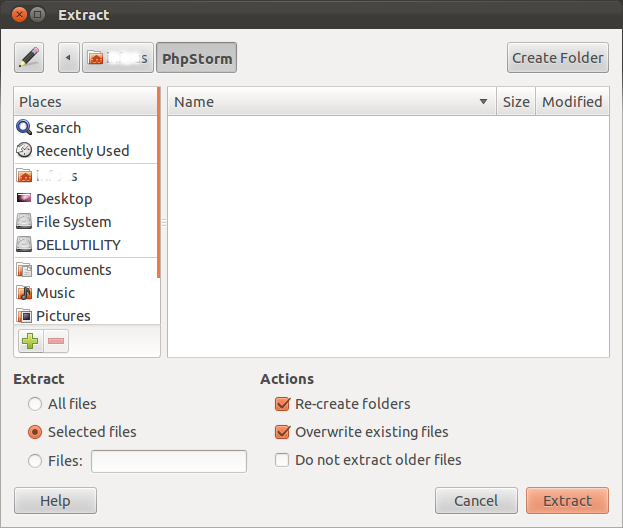
Don’t uncheck “Re-create folders” and “Overwrite existing files”. Everything should be like on the screenshots above. Otherwise the folder structure will be broken and you might get the error, when you’re launching phpstorm.sh:
Error: Could not find or load main class com.intellij.idea.Main
4. After the PhpStorm archive has been extracted quit the Archive Manager.
5. Open the Terminal and find phpstorm.sh inside ~/PhpStorm/PhpStorm-121.390/bin/ folder and run it:
sudo ~/PhpStorm/PhpStorm-121.390/bin/phpstorm.sh |
Congratulations, PhpStorm should be installed and launched!
Configure Postfix only to send mail
Very often you need to send mail only. For example, your web site sends some notifications by email only. In this case, there’s a reason to configure you MTA (main transfer agent) only to send emails.
In case of Postfix, only some options should be edited to force your Postfix to send mail only.
/etc/postfix/main.cf
inet_interfaces = loopback-only mydestination = |
Comment existing inet_interfaces and mydestination if they’re exist by using # at the beginning of the line.
Don’t forget to reload Postfix:
sudo /etc/init.d/postfix reload |
For more information you may read Postfix on a null client.
How to install Postfix on Ubuntu
Here’s a quick guide of installing Postfix (Mail Transfer Agent) on Ubuntu Linux.
To install Postfix type this command:
sudo apt-get install postfix |
/etc/postfix/main.cf is a main configuration file.
At least, configure a hostname in main.cf.
To find out the value of some configuration option type this command, for example, find out the myhostname value:
postconf -d myhostname
|
After all the changes have been made to main.cf you should restart the Postfix to apply the changes:
sudo /etc/init.d/postfix reload |
sendmail command examples
Before all of the things you need Linux and something like Postfix installed. I test these examples on Ubuntu.
In the first example, we will create a file with the message and then we’ll send it to the recipient with help of sendmail command.
Create the file /tmp/mail.txt that contains the text and a new line at the end:
sudo nano /tmp/mail.txt |
Subject: the subject This is the text of the message. [new line] |
Then type this:
sendmail recipient@gmail.com < /tmp/mail.txt |
GD extension required
I’ve tryed to use some GD functions in php. Locally everything is ok, I use xampp on Windows. But when I moved my site to the server I get this error:
PHP Fatal error: Uncaught exception ‘WideImage_Exception’ with message ‘WideImage requires the GD extension, but it’s apparently not loaded…
In my php app the WideImage library is used and it utilizes GD library. So, there isn’t GD extension installed. Well, let’s install it:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade --show-upgraded apt-get install php5-gd |
After installing php5 gd library the error have been gone and WideImage classes begin to work properly.
PHP has lots of libraries and modules. To list them you can use this command:
apt-cache search php5-
|
Then you will see:
php5-cgi - server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (CGI binary) php5-cli - command-line interpreter for the php5 scripting language php5-common - Common files for packages built from the php5 source php5-curl - CURL module for php5 php5-dbg - Debug symbols for PHP5 php5-dev - Files for PHP5 module development php5-gd - GD module for php5 php5-gmp - GMP module for php5 php5-ldap - LDAP module for php5 php5-mysql - MySQL module for php5 [...] |
If you want to install a module run the command:
sudo apt-get install module-or-library-name |
It’s possible to install several modules or libraries at once just separate them with a space.
Cron timezone problem
I’ve just tried to understand what’s the problem with my crontab. I set it to a proper time but nothing happens. As i guessed the problem is in timezone.
I use Debian linux so here I’ll provide steps how I’ve fixed it:
Configure time zone with dpkg-reconfigure
dpkg-reconfigure tzdata |
Link localtime to a corresponding zoneinfo file
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Kiev /etc/localtime |
In your case select your time zone.
Restart cron daemon
/etc/init.d/cron restart |
In my case this was the fix for the problem. I edited my contab and cron started to work like a Swiss watch ![]()